Dubbo
Dubbo(读音[ˈdʌbəʊ])是阿里巴巴公司开源的一个高性能优秀的服务框架,致力于提供高性能和透明化的 RPC 远程服务调用方案,以及 SOA 服务治理方案,使得应用可通过高性能的 RPC 实现服务的输出和输入功能,可以和 Spring框架无缝集成。 Dubbo是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。本文
参考文章:
Dubbo
什么是Dubbo
Dubbo 是一个分布式服务框架,致力于提供高性能和透明化的 RPC 远程服务调用方案,以及 SOA 服务治理方案,支持多种传输和序列化方案。Dubbo最常用的应用就是远程调用。 官网地址:http://dubbo.apache.org
Dubbo中服务端最核心的对象有四个:
- ApplicationConfig:配置当前应用信息
- ProtocolConfig:配置提供服务的协议信息
- RegistryConfig:配置注册相关信息
- ServiceConfig:配置暴露的服务信息
Dubbo客户端中核心的对象有两个:
- ApplicationConfig:配置当前应用信息
- ReferenceConfig:配置引用的服务信息
核心部件
Remoting:网络通信框架,实现了 sync-over-async 和 request-response 消息机制
RPC:一个远程过程调用的抽象,支持负载均衡、容灾和集群功能
Registry:服务目录框架用于服务的注册和服务事件发布和订阅
Dubbo是为了解决什么问题
- 当服务越来越多时,服务URL配置管理变得非常困难,F5硬件负载均衡器的单点压力也越来越大。
- 当进一步发展,服务间依赖关系变得错踪复杂,分不清哪个应用要在哪个应用之前启动,架构师都不能完整描述应用的架构关系。
- 接着,服务的调用量越来越大,服务的容量问题就暴露出来,这个服务需要多少机器支撑?什么时候该加机器?
Dubbo原理
架构
节点角色
Provider:暴露服务方称之为服务提供者
Consumer:调用远程服务方称之为服务消费者
Container:服务运行容器
Registry:服务注册与发现的中心目录服务称之为服务注册中心
Monitor:统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的日志服务称之为服务监控中心
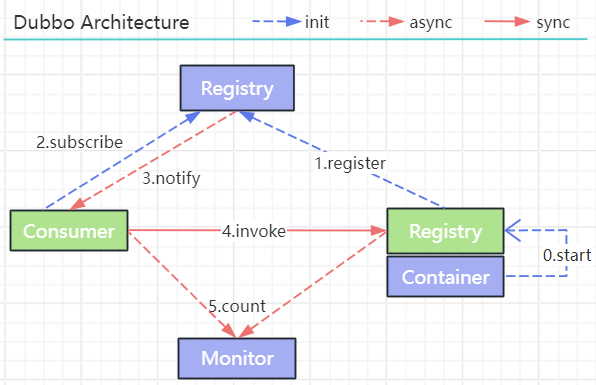
工作过程(Dubbo服务启动,调用,暴露消费的过程):
- 服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
- 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
- 服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
- 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者
- 注册中心,服务提供者,服务消费者三者之间均为长连接,监控中心除外。
- 注册中心通过长连接感知服务提供者的存在,服务提供者宕机,注册中心将立即推送事件通知消费者。
- 注册中心和监控中心全部宕机,不影响已运行的提供者和消费者,消费者在本地缓存了提供者列表。
- 服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
- 服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
Dubbo层(10层):
- 服务接口层(
Service):该层是与实际业务逻辑相关的,根据服务提供方和服务消费方的业务设计对应的接口和实现。 - 配置层(
Config):对外配置接口,以ServiceConfig和ReferenceConfig为中心- 可以直接
new配置类,也可以通过spring解析配置生成配置类。
- 可以直接
- 服务代理层(
Proxy):负责服务注册与查询服务,以及注册服务的本地缓存。- 服务接口透明代理,生成服务的
客户端Stub和服务器端Skeleton,以ServiceProxy为中心,扩展接口为ProxyFactory。
- 服务接口透明代理,生成服务的
- 服务注册层(
Registry):负责生成消费者的代理对象和服务提供方的Invoker。- 封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务URL为中心,扩展接口为
RegistryFactory、Registry和RegistryService。 - 可能没有服务注册中心,此时服务提供方直接暴露服务。
- 封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务URL为中心,扩展接口为
- 集群层(
Cluster):负责负载均衡的策略,以及失败的策略。- 封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以Invoker为中心,扩展接口为
Cluster、Directory、Router和LoadBalance。将多个服务提供方组合为一个服务提供方,实现对服务消费方来透明,只需要与一个服务提供方进行交互。
- 封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以Invoker为中心,扩展接口为
- 监控层(
Monitor):RPC调用次数和调用时间监控,以Statistics为中心,扩展接口为MonitorFactory、Monitor和MonitorService。 - 远程调用层(
Protocol):封将RPC调用,支持多种RPC协议(不包含IO通信部分)。以Invocation和Result为中心,扩展接口为Protocol、Invoker和Exporter。Protocol是服务域,它是Invoker暴露和引用的主功能入口,它负责Invoker的生命周期管理。Invoker是实体域,它是Dubbo的核心模型,其它模型都向它靠扰,或转换成它,它代表一个可执行体,可向它发起invoke调用,它有可能是一个本地的实现,也可能是一个远程的实现,也可能一个集群实现。
- 信息交换层(
Exchange):封装请求响应模式,同步转异步。- 处理各种协议的通信请求,支持
netty、mina、http等,默认采用netty进行通信。 - 以
Request和Response为中心,扩展接口为Exchanger、ExchangeChannel、ExchangeClient和ExchangeServer。
- 处理各种协议的通信请求,支持
- 网络传输层(
Transport):抽象mina和netty为统一接口,以Message为中心,扩展接口为Channel、Transporter、Client、Server和Codec。 - 数据序列化层(
Serialize):数据序列化层和可复用的一些工具,dubbo 协议缺省为 hessian2,rmi 缺省为 java,http 缺省为 json。扩展接口为Serialization、 ObjectInput、ObjectOutput和ThreadPool。
- 服务接口层(
启动时检查
- Dubbo 缺省会在启动时检查依赖的服务是否可用,不可用时会抛出异常,阻止 Spring 初始化完成,以便上线时,能及早发现问题,默认 check=“true”。
- 可以通过 check=“false” 关闭检查,比如,测试时,有些服务不关心,或者出现了循环依赖,必须有一方先启动。
- 另外,如果你的 Spring 容器是懒加载的,或者通过 API 编程延迟引用服务,请关闭 check,否则服务临时不可用时,会抛出异常,拿到 null 引用,如果 check=“false”,总是会返回引用,当服务恢复时,能自动连上。
集群容错
在集群调用失败时,Dubbo 提供了多种容错方案,缺省为 failover 重试。
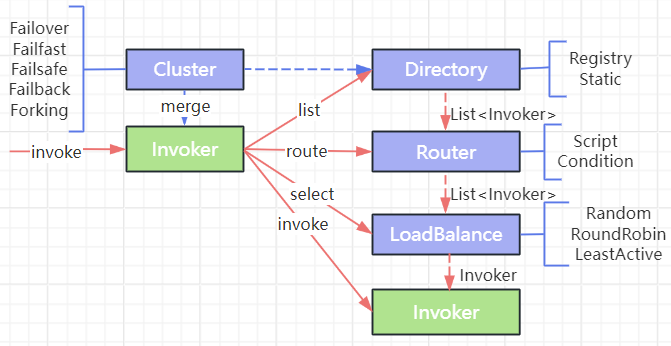
各节点的关系
Invoker是 Provider 的一个可调用 Service 的抽象,Invoker 封装了 Provider 地址及 Service 接口信息。Directory代表多个 Invoker,可以把它看成 List ,但与 List 不同的是,它的值可能是动态变化的,比如注册中心推送变更。Cluster将 Directory 中的多个 Invoker 伪装成一个 Invoker,对上层透明,伪装过程包含了容错逻辑,调用失败后重试另一个。Router负责从多个 Invoker 中按路由规则选出子集,比如读写分离,应用隔离等。LoadBalance负责从多个 Invoker 中选出具体的一个用于本次调用,选的过程包含了负载均衡算法,调用失败后,需要重选。
集群容错模式
Failover Cluster:失败自动切换(默认),当出现失败,重试其它服务器。
通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。可通过 retries=“2” 来设置重试次数(不含第一次)。由
FailoverClusterInvoker实现,原理是先获得retries的值,再通过for循环依次调用服务,如果成功则返回,如果失败则循环调用直至循环结束。Failfast Cluster:快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错。
通常用于非幂等性的写操作,比如新增记录。由
FailfastClusterInvoker实现,原理是直接调用一次。Failsafe Cluster:失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略。
通常用于写入审计日志等操作。由
FailsaveClusterInvoker实现。Failback Cluster:失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发。
通常用于消息通知操作。由
FailbackClusterInvoker实现,原理是,执行调用,出现异常后把错误放入ConcurrentHashMap,用任务调度线程池延迟5秒来重新执行调用,如果再失败,记录日志,不再调用。Forking Cluster:并行调用多个服务器,只要一个成功即返回。
通常用于实时性要求较高的读操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。可通过 forks=“2” 来设置最大并行数。
Broadcast Cluster:广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。
通常用于通知所有提供者更新缓存或日志等本地资源信息。
负载均衡
(1)随机(Random LoadBalance)按照权重设置随机概率(默认)。
(2)轮询(RoundRobin LoadBalance)
(3)最少活跃调用数(LeastActive LoadBalance),相同活跃调用数的随机
(4)一致性Hash(ConsistencyHash LoadBalance)一致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一提供者
多协议
Dubbo 允许配置多协议,在不同服务上或者同一服务上同时支持多种协议。
在不同服务上支持不同协议
不同服务在性能上适用不同协议进行传输,比如大数据用短连接协议,小数据大并发用长连接协议1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<dubbo:registry id="registry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" username="admin" password="hello1234" />
<!-- 多协议配置 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:protocol name="rmi" port="1099" />
<!-- 使用dubbo协议暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" ref="helloService" protocol="dubbo" />
<!-- 使用rmi协议暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.DemoService" version="1.0.0" ref="demoService" protocol="rmi" />
</beans>在同一服务上支持多种协议
需要与 http 客户端互操作1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<dubbo:registry id="registry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" username="admin" password="hello1234" />
<!-- 多协议配置 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:protocol name="hessian" port="8080" />
<!-- 使用多个协议暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:service id="helloService" interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" protocol="dubbo,hessian" />
</beans>
| 协议 | 稳定性 | 优点 | 缺点 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dubbo协议 | Stable | 采用NIO复用单一长连接,并使用线程池并发处理请求,减少握手和加大并发效率,性能较好(推荐使用) | 在大文件传输时,单一连接会成为瓶颈 | 可用于生产环境 |
| Rmi协议 | Stable | 可与原生RMI互操作,基于TCP协议 | 偶尔会连接失败,需重建Stub | 可用于生产环境 |
| Hessian协议 | Stable | 可与原生Hessian互操作,基于HTTP协议 | 需hessian.jar支持,http短连接的开销大 | 可用于生产环境 |
此外还支持webservice、http、Thrift、memcached、redis、rest等协议。
Dubbo序列化
| 协议 | 稳定性 | 优点 | 缺点 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hessian Serialization | Stable | 性能较好,多语言支持(推荐使用) | Hessian的各版本兼容性不好,可能和应用使用的Hessian冲突,Dubbo内嵌了hessian3.2.1的源码 | 可用于生产环境 |
| Dubbo Serialization | Stable | 通过不传送POJO的类元信息,在大量POJO传输时,性能较好 | 当参数对象增加字段时,需外部文件声明 | 试用 |
| Json Serialization | Stable | 纯文本,可跨语言解析,缺省采用FastJson解析 | 性能较差 | 试用 |
| Java Serialization | Stable | Java原生支持 | 性能较差 | 可用于生产环境 |
注册中心
Dubbo 支持同一服务向多注册中心同时注册,或者不同服务分别注册到不同的注册中心上去,甚至可以同时引用注册在不同注册中心上的同名服务。另外,注册中心是支持自定义扩展的。
| 协议 | 稳定性 | 优点 | 缺点 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zookeeper注册中心 | Stable | 支持基于网络的集群方式,有广泛周边开源产品,建议使用dubbo-2.3.3以上版本(推荐使用) | 依赖于Zookeeper的稳定性 | 可用于生产环境 |
| Redis注册中心 | Stable | 支持基于客户端双写的集群方式,性能高 | 要求服务器时间同步,用于检查心跳过期脏数据 | 可用于生产环境 |
| Multicast注册中心 | Tested | 去中心化,不需要安装注册中心 | 依赖于网络拓扑和路由,跨机房有风险 | 小规模应用或开发测试环境 |
| Simple注册中心 | Tested | Dogfooding,注册中心本身也是一个标准的RPC服务 | 没有集群支持,可能单点故障 | 试用 |
Dubbo服务降级
可以通过服务降级功能 临时屏蔽某个出错的非关键服务,并定义降级后的返回策略。
服务降级就是当服务响应超时或连接请求超时,不用继续等下去,而采用降级措施,返回一个我们自己定义好的提示。而为什么要使用服务降级,这是防止分布式服务发生雪崩效应。当一个请求发生超时,一直等待着服务响应,那么在高并发情况下,很多请求都是因为这样一直等着响应,直到服务资源耗尽产生宕机,而宕机之后会导致分布式其他服务调用该宕机的服务也会出现资源耗尽宕机,这样下去将导致整个分布式服务都瘫痪。集群环境下,当一台服务宕机之后,其他流量分发到其他集群机器上,压力也会随之加大,时间久了整个集群也会垮了,这只是个时间问题。为了防止产生了雪崩效应那么就该对服务配置降级,一旦请求超过规定时间立即返回自定义好的提示,无需继续等待。
dubbo中有提供一个叫做mock的配置,mock只在出现非业务异常(比如超时,网络异常等)时执行。mock的配置支持两种:
(1)采用return null,返回简单的空
打开项目里的consumer.xml修改dubbo:reference配置即可:
1 | <dubbo:reference id="userService" check="false" interface="com.cwh.service.UserService" timeout="3000" mock="return null"/> |
在服务提供者例如UserServiceImpl中的getUser方法打个断点来模拟请求超时。然后浏览器访问,断点不过,一致等待,当时间超过3秒,直接返回了空,这样就已经实现了一个简单的服务降级了
(2)采用自定义提示
1 | <dubbo:reference id="userService" check="false" interface="com.cwh.service.UserService" timeout="3000" mock="true"/> |
在service包下也就是同UserService目录下新建一个UserServiceMock,注意这里名字一点要是该接口名+Mock:
1 | public class UserServiceMock implements UserService{ |
Dubbo灰度发布
当一个接口实现,出现不兼容升级时,可以用版本号过渡,版本号不同的服务相互间不引用,用法如下:
1 | <dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoService" version="1.0.0" /> |
利用dubbo该特性,我们能够实现一些功能的灰度发布,实现步骤如下:
- 接口旧的实现定义version=“1.0.0”,接口新的实现version=“2.0.0”
- Consumer端定义version=”*”
- 这样定义Provider和Consumer后,新旧接口实现各承担50%的流量
- 利用dubbo该特性,还能完成不兼容版本迁移:
- 在低压力时间段,先升级一半Provider为新版本;
- 再将所有消费者升级为新版本;
- 然后将剩下的一半提供者升级为新版本。
Dubbo异步调用
默认是同步等待结果阻塞的,支持异步调用。通过asyanc属性设置异步,若设置异步,则无需等待该方法返回值,程序即可往下进行。
1 | Object o = Methoda(); |
(1) 打印结果为null (2) Timeout不会超时,所以不会重试
Dubbo 是基于 NIO 的非阻塞实现并行调用,客户端不需要启动多线程即可完成并行调用多个远程服务,相对多线程开销较小,异步调用会返回一个 Future 对象。异步调用流程图如下:
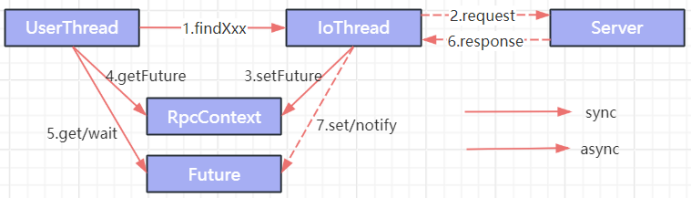
Dubbo实践
Dubbo快速入门
- 创建服务提供者
Provider模块 - 创建服务消费者
Consumer模块 - 在服务提供者模块编写
UserServiceImpl提供服务 - 在服务消费者中的
UserController远程调用UserServiceImpl提供的服务 - 分别启动两个服务,测试
企业中如何通过Dubbo实现分布式调用
在企业中,如果消费者直接通过RPC去调用提供者,理论上需要把提供者的整个Jar包引入到项目中。但是这样的话服务提供这种的其他无关代码也会被引入其中,导致代码污染。
因此实际开发过程中,服务提供者和调用者之间会增加一层Client模块。这个Client中主要写的是Service的接口定义,接口的返回实例对象以及接口的请求实例对象。简单来讲,所有的定义都在Client中完成。 使用时,服务提供者引入这个Client,然后写实现方法,服务消费者引入这个Client,然后通过dubbo直接调用即可。
另外企业开发中,可能会出现多个接口实现,这种情况下可以给Service设定group、version等进行区分。
dubbo-client 模块
定义一个公共的客户端服务,命名为dubbo-client,这个服务里存放的是service接口,整体代码结构如下:
1 | dubbo-client |
UserService接口:
1 | // 接口类 |
dubbo-provider 模块
服务提供者引入 dubbo-client 工程,写实现类,提供dubbo接口,见后文配置文件编写。
服务提供者需要写服务的实现类,这里需要注意**@Service注解采用的是dubbo包下**:
1 | import com.javayz.client.entity.User; |
接着在启动类上添加一个@EnableDubbo注解:
1 |
|
dubbo-consumer 模块
服务消费者引入 dubbo-client 工程,通过这个工程的service接口调用,见后文配置文件编写。
服务的消费者同样是先编辑好配置文件,如上,接着通过**@Reference注解将service对象引进来**:
1 |
|
provider 与 consumer 配置文件
pom.xml
1 | <dependencies> |
SpringBoot方式
application.properties
1 | dubbo.application.name=dubbo-provider |
或者 application.yml
1 | dubbo: |
Spring方式
在resource文件夹下新建两个配置文件: provider.xml
1 |
|
consumer.xml
1 | <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" |
接着是服务的提供者和消费者配置注入:
1 | // 服务提供者 |
dubbo的常用配置
1 | <dubbo:application/> 用于配置当前应用信息 |
直接代码
引入依赖
1 | <dependencies> |
编写服务提供者
服务提供者主要配置以下几个属性:
- **
application**:设置应用的名称等信息 - **
protocol**:设置服务的协议 - **
register**:设置服务的连接方式 - **
service**:将需要暴露的服务注册出来
1 | public class DubboProvider { |
编写服务消费者
消费者的实现主要就三步:
- 配置
application:设置应用的名称等信息 - 配置
reference:主要配置要引用的信息 - 获取到接口,调用服务。
1 | public class DubboConsumer { |
先启动提供者,再启动消费者,如果user信息打印出来了就说明调用成功。
Dubbo & Spring Cloud
Dubbo特点
- 远程通讯:提供对多种基于长连接的 NIO 框架抽象封装(非阻塞 I/O 的通信方式,Mina/Netty/Grizzly),包括多种线程模型,序列化(Hessian2/ProtoBuf),以及“请求-响应”模式的信息交换方式。
- 集群容错:提供基于接口方法的透明远程过程调用(RPC),包括多协议支持(自定义 RPC 协议),以及软负载均衡(Random/RoundRobin),失败容错(Failover/Failback),地址路由,动态配置等集群支持。
- 自动发现:基于注册中心目录服务,使服务消费方能动态的查找服务提供方,使地址透明,使服务提供方可以平滑增加或减少机器。
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud 基于 Spring Boot,为微服务体系开发中的架构问题,提供了一整套的解决方案——服务注册与发现,服务消费,服务保护与熔断,网关,分布式调用追踪,分布式配置管理等。
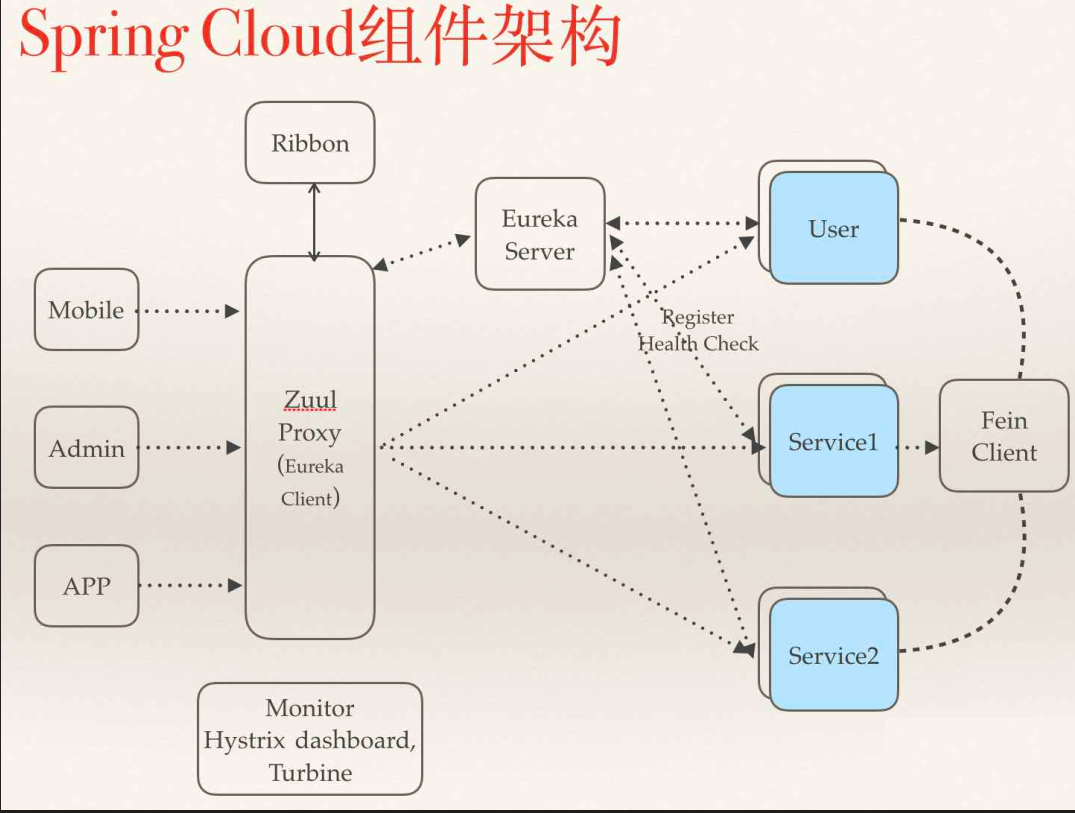
Dubbo vs Spring Cloud
| Dubbo | Spring Cloud | |
|---|---|---|
| 服务注册中心 | Zookeeper | Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka |
| 服务调用方式 | RPC | REST API |
| 服务监控 | Dubbo-monitor | Spring Boot Admin |
| 断路器 | 不完善 | Spring Cloud Netflix Hystrix |
| 服务网关 | 无 | Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul |
| 分布式配置 | 无 | Spring Cloud Config |
| 服务跟踪 | 无 | Spring Cloud Sleuth |
| 消息总线 | 无 | Spring Cloud Bus |
| 数据流 | 无 | Spring Cloud Stream |
| 批量任务 | 无 | Spring Cloud Task |
| …… | …… | …… |
使用 Dubbo 构建的微服务架构就像组装电脑,各环节的选择自由度很高,但最终结果很有可能因为一条内存质量不行就点不亮了;而 Spring Cloud 就像品牌机,在 Spring Source 的整合下,做了大量的兼容性测试,保证了机器拥有更高的稳定性,但若要在使用非原装组件外的东西,就需要对其基础有足够的了解。
Spring Cloud是真正的微服务框架、提供整套的组件支持、使用简单方便、强大的社区支持等等,另外考虑到 .NET/.NET Core 的兼容处理,RPC 并不能很好的实现跨语言(需要借助跨语言库,比如 gRPC、Thrift,但因为 Dubbo 本身就是“gRPC”,在 Dubbo 之上再包一层 gRPC,有点重复封装了),而 HTTP REST 本身就是支持跨语言实现,所以,Spring Cloud 这一点还是非常好的(Dubbox 也支持,但性能相比要差一些)。
凡事无绝对,每件事物有好的地方也有不好的地方,总的来说,Dubbo 和 Spring Cloud 的主要不同体现在两个方面:服务调用方式不同和专注点不同(生态不同)。



